OpenAI dropped GPT-5.2 this morning, and if you've been building AI agents or wrestling with production tool-calling workflows, you're going to want to pay attention. This isn't a flashy consumer release—it's an infrastructure upgrade designed for developers who need AI systems that can reliably execute multi-step tasks, handle complex tool chains, and operate at scale without constant supervision.
After Google's Gemini 3 topped leaderboards last month and triggered Sam Altman's internal "code red" memo, GPT-5.2 arrives as OpenAI's most aggressive push yet into enterprise and developer-focused AI. The improvements center on exactly what matters when you're shipping code that calls external APIs, queries databases, or orchestrates tool chains: accuracy, token efficiency, and the ability to plan across long contexts without losing the thread.
The Numbers That Matter: GPT-5.2 vs. 5.1 vs. 5.0
Let's cut through the marketing speak and look at what changed between these three releases. The progression from GPT-5.0 (August 2025) through 5.1 (November) to today's 5.2 reflects a deliberate path toward production reliability rather than research benchmarks.
Benchmark Performance Comparison
| Benchmark | GPT-5.0 | GPT-5.1 | GPT-5.2 | What It Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWE-Bench Verified | 69.1% | 76.3% | 80.0% | Real-world software engineering tasks |
| GDPval (Professional Tasks) | 38.8% | 38.8% | 70.9% | Expert-level knowledge work accuracy |
| τ2-bench (Tool Calling - Telecom) | Not available | 95.6% | 98.7% | Multi-step tool orchestration |
| SWE-Bench Pro | Not available | 50.8% | 55.6% | Complex coding with multiple languages |
| GPQA Diamond (Science) | Not available | 88.1% | 92.4% | PhD-level scientific reasoning |
| Hallucination Rate | Not available | 8.8% | 6.2% | Response-level error frequency |
The jump from GPT-5.1 to 5.2 on professional knowledge work is particularly striking: 70.9% means the model now beats or ties human experts on these tasks more than two-thirds of the time. That's not an incremental gain—it's the difference between "needs oversight" and "can operate semi-autonomously."
What Changed Under the Hood
GPT-5.0 (August 2025) introduced the unified reasoning architecture with distinct "Instant" and "Thinking" modes. The model could switch between fast responses and deeper reasoning, but the tool-calling behavior was inconsistent, and token efficiency on agentic workflows lagged behind specialized models.
GPT-5.1 (November 2025) made the system more conversational and customizable. The "Instant" variant gained adaptive reasoning—the ability to automatically pause and think when encountering complex questions without explicit prompting. Latency improved, with 5.1 Thinking roughly twice as fast on straightforward tasks and more deliberate on complex ones.
GPT-5.2 (December 2025) is where everything clicks for production use. According to OpenAI's official release, this version delivers "significant improvements in general intelligence, long-context understanding, agentic tool-calling, and vision—making it better at executing complex, real-world tasks end-to-end than any previous model."
Why Tool Calling Performance Actually Matters
If you've built an AI agent that needs to search a database, call an API, process the results, and then make another decision based on those results, you've experienced the pain of unreliable tool calling. The model hallucinates function arguments. It calls the wrong tool. It forgets context between tool invocations. It tries to call six tools in parallel when three of them depend on the results of the first.
GPT-5.2's 98.7% accuracy on τ2-bench telecom tasks represents something tangible: the model can now chain together tool calls across multiple steps with high reliability. Companies like Notion, Box, Shopify, and Harvey reported observing "state-of-the-art long-horizon reasoning and tool-calling performance" during early testing.
Real-World Tool Calling Example
Here's what improved tool-calling looks like in practice. When a customer reports a delayed flight, a missed connection, an overnight stay, and a medical seating requirement, GPT-5.2 manages the entire chain of tasks—rebooking, special-assistance seating, and compensation—delivering a more complete outcome than GPT-5.1.
The model achieved 98.7% on τ2-bench Telecom (up from 95.6% in GPT-5.1) and 82.0% on τ2-bench Retail (up from 77.9%), demonstrating its ability to reliably use tools across long, multi-turn customer support scenarios.
Token Efficiency in Agentic Workflows
Here's a metric that directly affects your AWS bill: on SWE-bench tasks, internal testing showed more efficient token usage compared to previous models. That's not just speed—it's operational cost. When you're running hundreds or thousands of agent sessions per day, those numbers compound fast.
The model also reduced hallucination rates by 30% on real-world queries compared to GPT-5.1 (from 8.8% to 6.2% error rate). Fewer errors mean fewer retries, less manual intervention, and more tasks completed successfully on the first attempt.
Long-Context Reasoning: Why This Unlocks New Workflows
GPT-5.2 is the first model to achieve near 100% accuracy on OpenAI's 4-needle MRCR variant test (out to 256k tokens). In practical terms, this means you can now feed the model entire codebases, multi-document research sets, or lengthy conversation histories without it losing critical details buried in the middle.
The implications for agentic systems are significant. When an AI agent needs to maintain coherence across a 200-page legal document or cross-reference information across dozens of API responses, long-context reliability stops being a nice-to-have and becomes a deployment requirement.
Long-Context Performance Breakdown
| Context Window | GPT-5.2 Thinking | GPT-5.1 Thinking |
|---|---|---|
| 4k–8k tokens (8 needles) | 98.2% | 65.3% |
| 16k–32k tokens (8 needles) | 95.3% | 44.0% |
| 64k–128k tokens (8 needles) | 85.6% | 36.0% |
| 128k–256k tokens (8 needles) | 77.0% | 29.6% |
These numbers matter when you're building agents that need to process entire documentation sets, analyze multi-file codebases, or synthesize information across dozens of API responses.
Connecting GPT-5.2 to Real-World Tools: The MCP Challenge
Here's where theory meets infrastructure reality. GPT-5.2's improved tool-calling abilities are only useful if you can actually connect it to your production systems—databases, SaaS APIs, internal services, cloud platforms. That's where the Model Context Protocol ecosystem comes in.
Companies like Klavis AI have been building production-ready infrastructure for exactly this problem. While GPT-5.2 provides the intelligence layer, developers still need secure, reliable connectors to translate model intentions into authenticated API calls across dozens of services.
The challenge isn't just technical—it's operational. When you're connecting AI agents to systems like GitHub, Slack, Notion, Salesforce, and Google Cloud simultaneously, you need:
- OAuth 2.0 handling across multiple providers
- Multi-tenancy support so different users can access their own data
- Rate limiting and error recovery that doesn't break the agent loop
- Structured logging for debugging when tool chains fail
This is infrastructure work that sits between the model and your business logic. GPT-5.2's enhanced tool-calling accuracy makes these integrations more reliable, but you still need the plumbing.
The Progressive Discovery Pattern
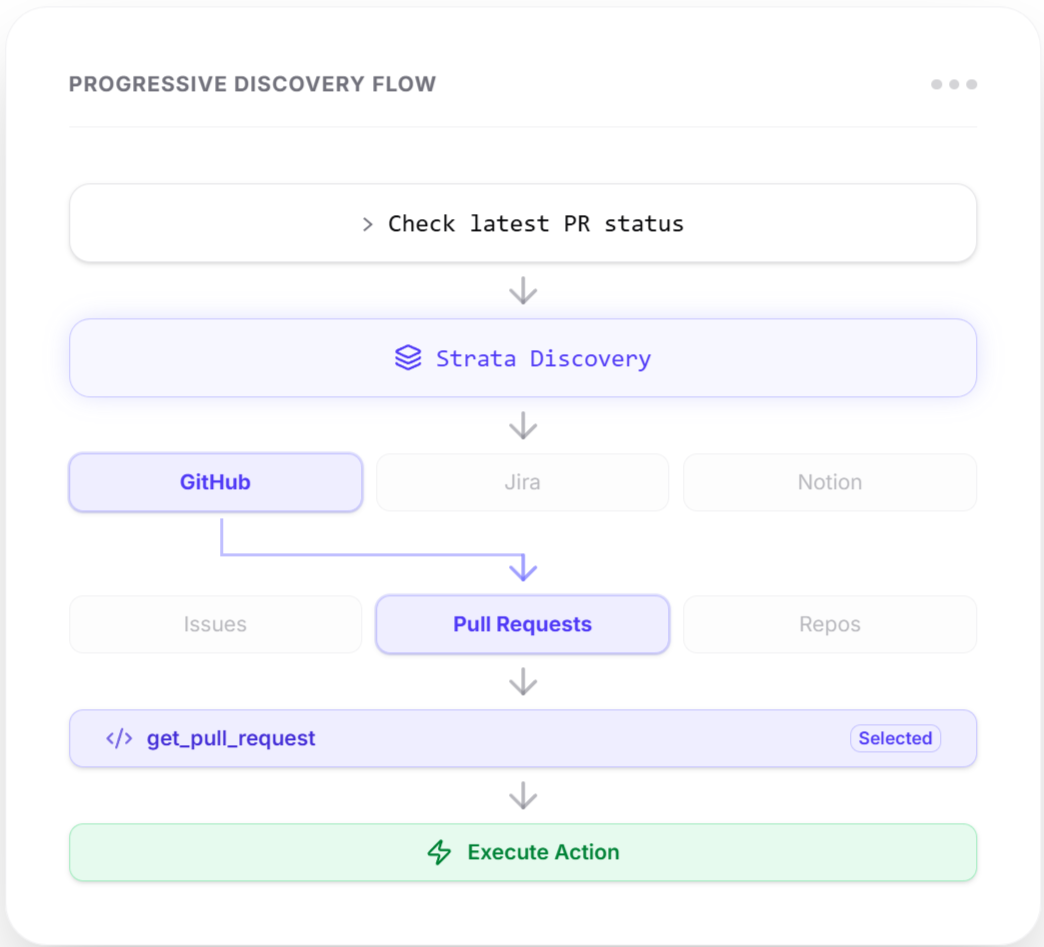
One of the more practical innovations in the MCP space is what Klavis AI calls "progressive discovery" through their Strata product. Instead of overwhelming GPT-5.2 with hundreds of available tools upfront (which empirically degrades performance), the system guides the model through a hierarchy:
- Intent recognition → What category of task?
- Category navigation → Which service handles this?
- Action selection → What specific API call?
- Execution → Invoke with proper parameters
Internal testing from companies deploying this pattern showed +13.4% pass@1 improvement on Notion tasks and +15.2% on GitHub workflows compared to standard MCP implementations. This matters because even GPT-5.2's 98.7% tool-calling accuracy can degrade when the search space becomes too large.
Practical Deployment Patterns for GPT-5.2 Agents
Based on early adoption patterns and OpenAI's own recommendations, here are the architectural patterns that make sense for production deployment:
1. Use the Responses API for Stateful Agents
GPT-5.2 works with both the Chat Completions API and the newer Responses API, but statistically significant improvements were observed when using Responses—especially for multi-turn agentic workflows. The Tau-Bench Retail score jumped from 73.9% to 78.2% just by switching APIs and properly passing chain-of-thought context between turns.
The Responses API handles tool calls, file processing, and structured outputs in a single request, eliminating manual orchestration layers that introduce latency and failure points.
2. Tune Reasoning Effort Based on Task Complexity
GPT-5.2 exposes a reasoning_effort parameter with settings including none, medium, high, and xhigh. For complex, multi-step tasks, OpenAI recommends higher reasoning to ensure the best possible outputs. In practice, this means routing simple database queries through medium reasoning but escalating complex refactoring tasks to xhigh.
Interestingly, GPT-5.2 Thinking at reasoning.effort='none' scored 57.2% on τ2-bench Telecom—substantially outperforming GPT-5.1 Thinking at 47.8% and GPT-4.1 at 49.2% on the same setting. This means even without extended reasoning, GPT-5.2 handles tool-calling tasks better than previous flagship models.
3. Break Complex Tasks Across Multiple Agent Turns
One counterintuitive finding: GPT-5.2 performs better when "distinct, separable tasks are broken up across multiple agent turns, with one turn for each task." Rather than asking it to "analyze this codebase, find bugs, fix them, and write tests" in one shot, structure it as separate calls: analyze → report findings → propose fixes → implement → test.
This pattern reduces the cognitive load per turn and makes debugging easier when something goes wrong midway through a workflow.
4. Implement Tool Preambles for Better Traceability
GPT-5.2 supports "preambles"—short explanations the model outputs before calling a tool. By adding a system instruction like "Before you call a tool, explain why you are calling it," you get dramatically better audit trails for debugging production issues.
Internal testing showed that preambles boost tool-calling accuracy and overall task success without bloating reasoning overhead. The model prepends a concise rationale to each tool call, making it easier to trace decisions when workflows fail.
Pricing Considerations
GPT-5.2 carries a price premium over previous models, but the token efficiency gains may offset the higher per-token cost:
| Model | Input (per 1M tokens) | Cached Input | Output (per 1M tokens) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-5.2 / GPT-5.2 Instant | $1.75 | $0.175 (90% off) | $14 |
| GPT-5.2 Pro | $21 | — | $168 |
| GPT-5.1 / GPT-5.1 Instant | $1.25 | $0.125 (90% off) | $10 |
The key calculation: if GPT-5.2 completes tasks more efficiently and requires fewer tool calls, your effective cost per completed task may actually decrease despite the higher nominal price.
For high-volume deployments, leverage the prompt caching feature—it can reduce repeated processing of long system prompts or context documents by 90%, which compounds quickly in agentic workflows.
FAQs
Q: Should I migrate from GPT-5.1 to GPT-5.2 immediately for production agents?
Not necessarily. GPT-5.1 remains available in the API with no current deprecation plans. Start with parallel testing—run the same agent workflows through both models and measure task completion rates, token usage, and error rates. The 5.2 improvements are substantial for complex tool-calling scenarios, but simpler workflows may not justify immediate migration.
Q: How do I handle the transition period while rolling out GPT-5.2?
Use feature flags and gradual rollout. Route a small percentage of traffic to GPT-5.2 initially (5-10%), monitor closely for a week, then increase incrementally. OpenAI's model router in Azure can automatically select between models based on task complexity, giving you dynamic optimization without manual routing logic.
Q: What's the single biggest mistake developers make when implementing agentic workflows with GPT-5.2?
Exposing too many tools at once. Even with GPT-5.2's improved accuracy, presenting 50+ tools upfront degrades selection accuracy. Use hierarchical tool organization (categories → services → actions) or progressive discovery patterns. This is where infrastructure solutions like Klavis AI's Strata server become practical—they implement these patterns as infrastructure rather than application logic.
Q: Does GPT-5.2 work with existing MCP servers, or do I need to upgrade infrastructure?
Existing MCP servers work fine with GPT-5.2. The improvements are model-side, not protocol-side. However, you may want to optimize your tool descriptions and schemas to take advantage of the enhanced instruction-following capabilities—clearer, more concise tool descriptions yield better results.
