Developers building autonomous agents currently face a critical friction point: testing against live production APIs is dangerous, expensive, and non-deterministic.
As AI labs and enterprises invest billions in developing sophisticated AI agents, the need for reliable training and evaluation infrastructure has never been greater. Reinforcement learning environments are emerging as the critical infrastructure powering the next generation of AI agent capabilities. Just as labeled datasets powered the last wave of AI breakthroughs, RL environments are becoming essential for training agents on complex, multi-step tasks.
Klavis Sandbox-as-a-Service eliminates the barrier between agent development and production safety by providing ephemeral, fully controllable application environments. It allows developers to spin up isolated instances of popular SaaS tools (like Google Calendar, Salesforce, or Slack), seed them with precise custom data, and interact with them using the Model Context Protocol (MCP)—all without touching real user data.
What is Klavis Sandbox-as-a-Service?
Klavis Sandbox-as-a-Service is a fully managed infrastructure platform that provides deterministic, reproducible environments for AI agent development. Unlike standard mock servers that return static responses, Klavis Sandboxes are stateful logic engines backed by real service instances.
To address the specific needs of enterprise AI development, Klavis Sandbox is built on three core pillars:
Key Features
Real Underlying Service: Unlike standard mocks that return static, pre-canned responses, Klavis Sandboxes rely on real service instances. This ensures 100% fidelity; when your agent executes a complex query or logic operation, the sandbox processes it exactly as the production service would, not just as a simulation.
Managed Lifecycle: We abstract away the infrastructure complexity. You do not need to manage Docker containers, authentication tokens, or database schemas. You simply use the Klavis API to request a sandbox, and we handle the provisioning, maintenance, and teardown automatically.
Native Parallelism: To support high-throughput testing and training, Klavis supports full parallelism. You can create multiple isolated sandboxes for the same service simultaneously. This allows you to run parallel evaluation suites or training epochs without fear of state collisions between different agents.
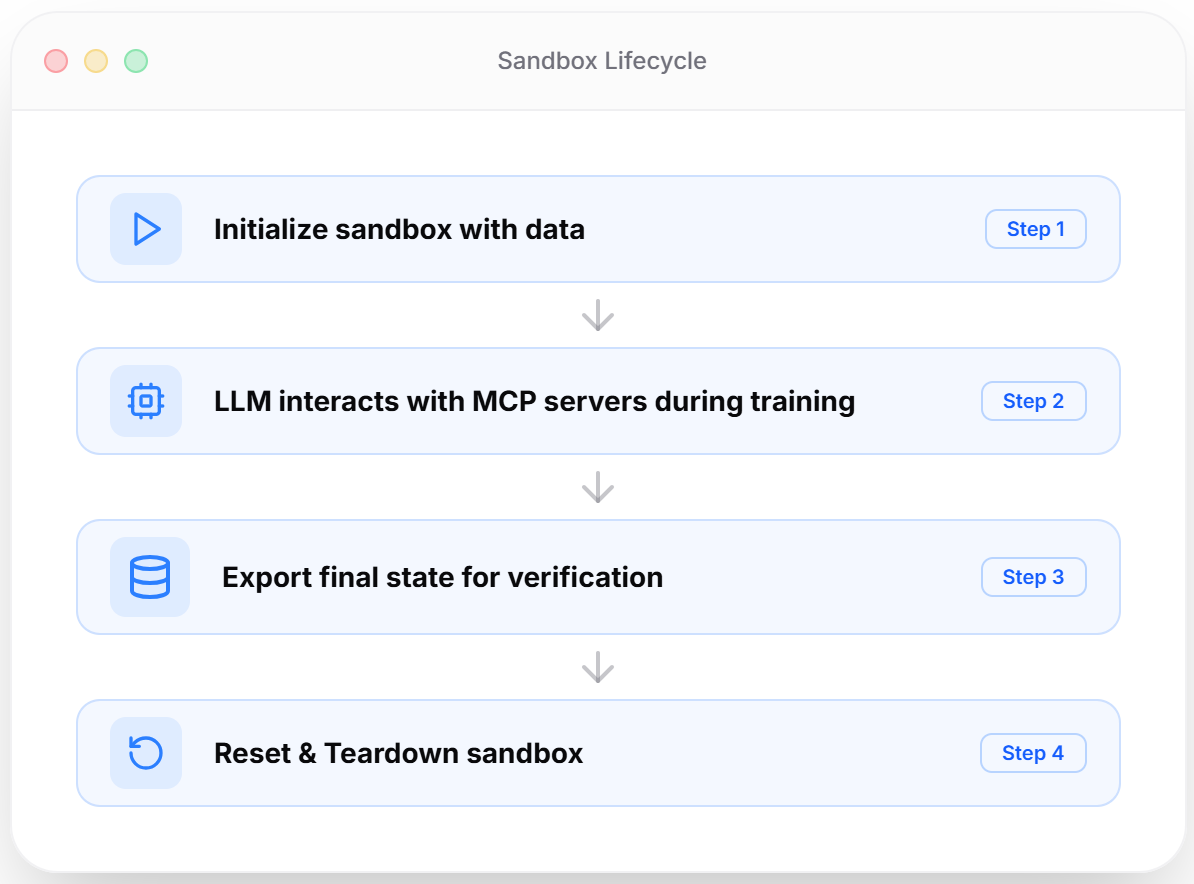
The Sandbox Lifecycle: Initialize, Interact, Dump, Reset
The core workflow of a Klavis Sandbox is designed for the rigorous demands of AI engineering:
Initialize (Seed): You send a JSON payload to define the exact "world state." For example, in a Google Calendar sandbox, you can inject specific mock events, attendees, and conflicts to create a controlled test scenario.
Interact (MCP): Your AI agent interacts with the sandbox using Klavis MCP tools. The agent perceives the sandbox as the real application, performing actions like
create_event,delete_file, orsend_message.Dump (Verify): At any point, you can snapshot the full state of the sandbox. This allows you to programmatically verify that the agent performed the intended action by comparing the "Dump" data against your expectations.
Reset: With a single API call, the sandbox wipes all data and returns to a pristine clean state, ready for the next test cycle.
Step-by-Step Guidance: The Lifecycle of a Sandbox Session
To demonstrate the power of deterministic infrastructure, let's look at a practical workflow using the Outlook Calendar Sandbox. In this scenario, we will initialize a calendar, verify the data, use an agent to modify it, and then prove the change occurred.
Step 0: Create the Sandbox
First, we use create sandbox API to create a new Outlook Calendar sandbox instance, and get the corresponding sandbox ID and MCP server.
Step 1: Initialize with Custom Data
We call the initialization endpoint. We need to provide a JSON payload that defines our events. The schema of the payload is documented in our API reference.
We've prepared a payload that creates 5 events. We can see in the backend account that the events are actually created in the Outlook Calendar. As a user, you will use the dump endpoint (see Step 2) to verify that.
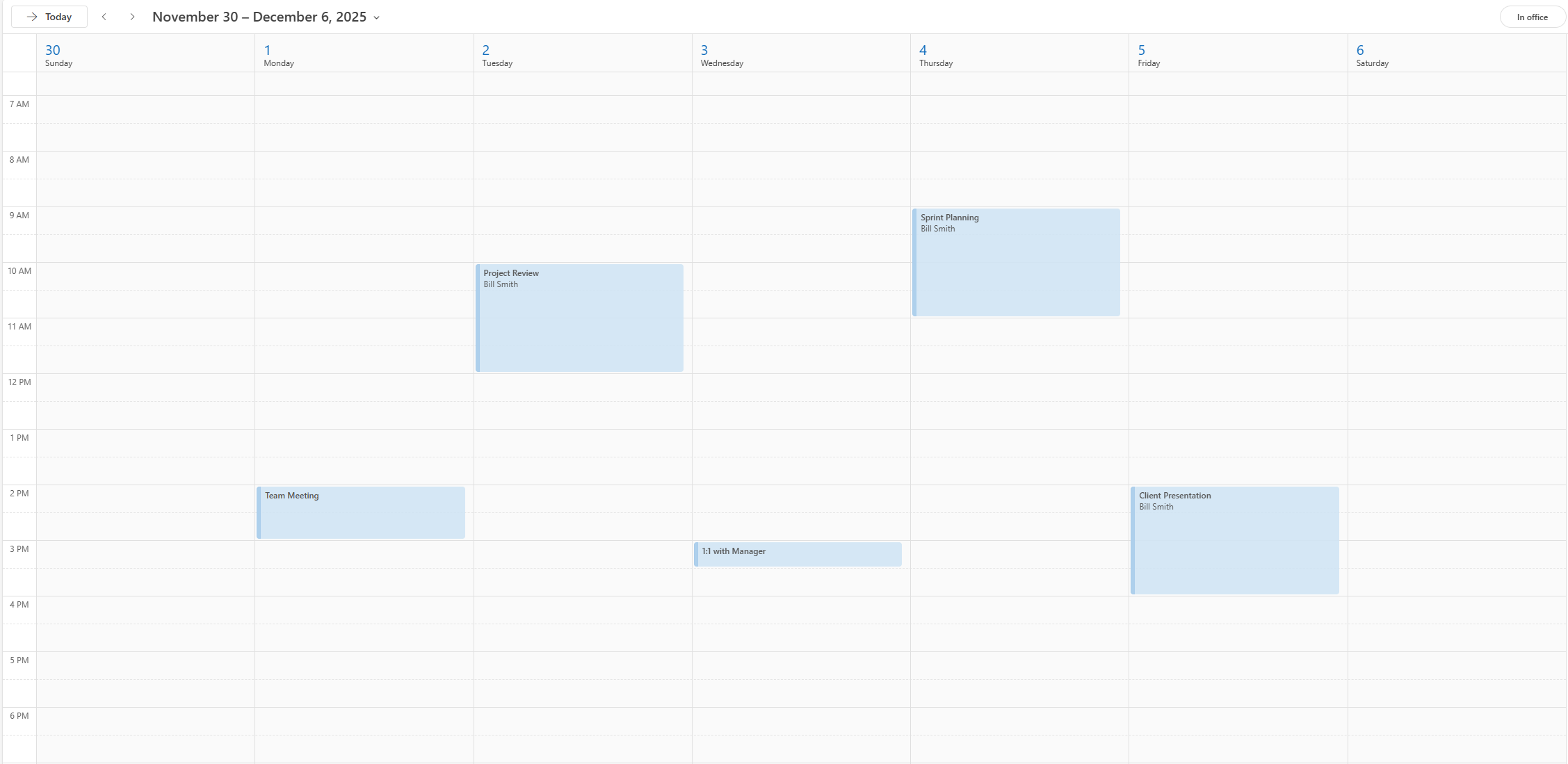
Step 2: Verify State (Optional)
Before the agent takes action, we establish our "Ground Truth." We use dump API to dump the sandbox data to confirm the initialization worked perfectly.
The API should return a JSON array with the 5 events we created in Step 1.
{
"events": [
{
"id": "AAMkAGJjMGYzMjk3LTMyMTMtNGM5Yy1iYzFkLTMzNGJkM2JmY2NjMgBGAAAAAACa_BXtkJHjT7S5_PVHou2NBwD3LHOA1yl-R6PG7mrkXNJPAAAAAAENAAD3LHOA1yl-R6PG7mrkXNJPAAABpsu7AAA=",
"subject": "Client Presentation",
"start": {
"dateTime": "2025-12-05T22:00:00.0000000",
"timeZone": "UTC"
},
"end": {
"dateTime": "2025-12-06T00:00:00.0000000",
"timeZone": "UTC"
},
"location": {
"displayName": "Zoom Meeting",
"locationType": "default",
"uniqueId": "Zoom Meeting",
"uniqueIdType": "private"
},
"attendees": [
"client@company.com",
"sales@example.com"
]
},
...
]
}
Step 3: Agent Interaction via MCP
Now, we let the AI agent perform actions on the sandbox, using the MCP we got from Step 0. Connect the MCP server to your agents (e.g., LangChain, CrewAI, Claude, OpenAI Agents SDK). We give the following prompt to modify the events:
Cancel the Sprint Planning meeting in my calendar, and move the 1-on-1 to the same time on next day.
We can see in the backend account the task is finished correctly.
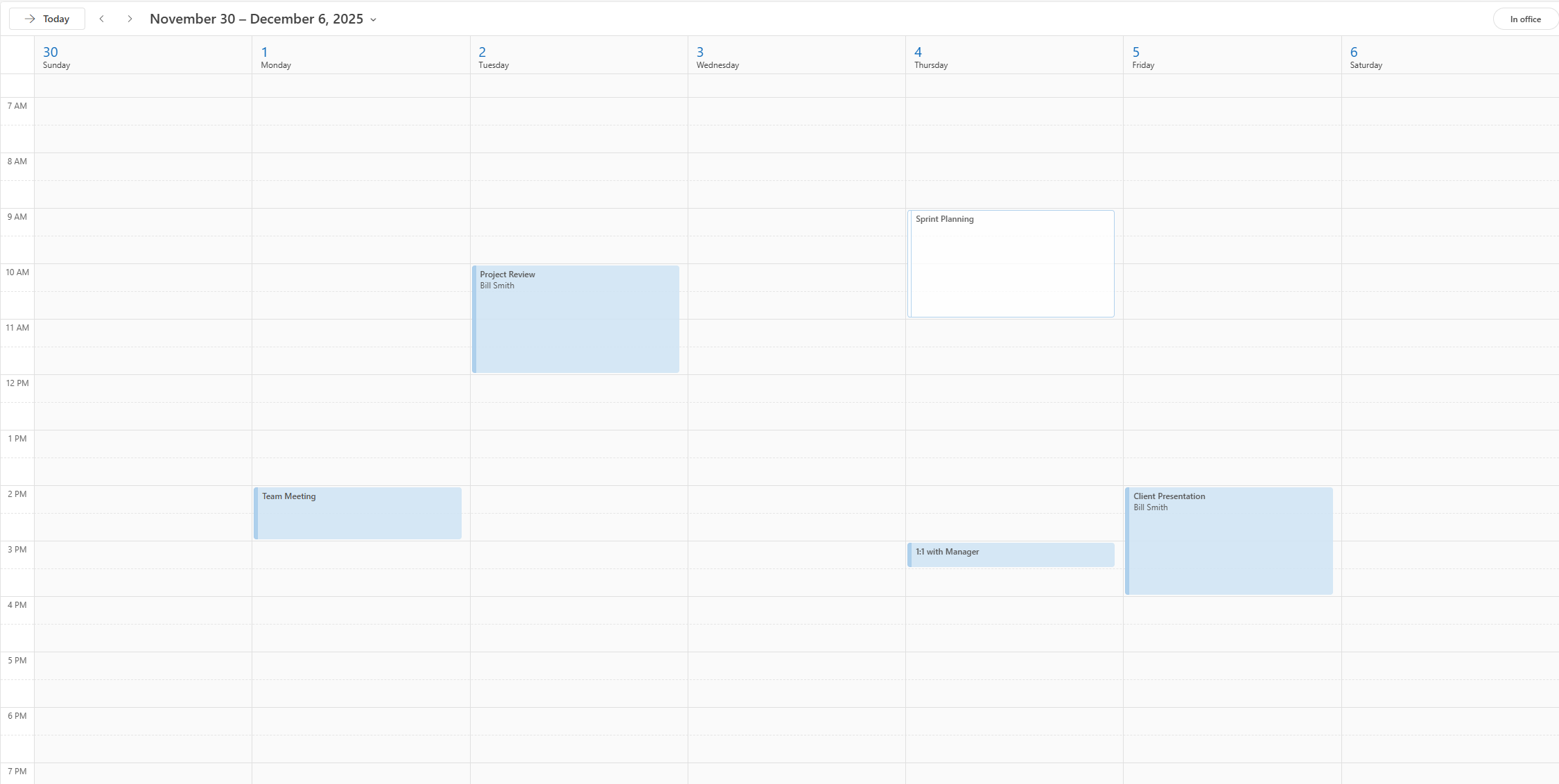
Step 4: Validate Changes
For sandbox users to verify the agent succeeded, we don't directly go to the backend account. Instead, we use the dump API again to get the current state of the calendar.
We should get 4 events now, with the Sprint Planning meeting removed and the 1-on-1 rescheduled to Dec 4.
{
"events": [
...
{
"id": "AAMkAGJjMGYzMjk3LTMyMTMtNGM5Yy1iYzFkLTMzNGJkM2JmY2NjMgBGAAAAAACa_BXtkJHjT7S5_PVHou2NBwD3LHOA1yl-R6PG7mrkXNJPAAAAAAENAAD3LHOA1yl-R6PG7mrkXNJPAAABpsu5AAA=",
"subject": "1:1 with Manager",
"start": {
"dateTime": "2025-12-04T23:00:00.0000000",
"timeZone": "UTC"
},
"end": {
"dateTime": "2025-12-04T23:30:00.0000000",
"timeZone": "UTC"
},
"location": {
"displayName": "",
"locationType": "default",
"uniqueIdType": "unknown",
"address": {},
"coordinates": {}
},
"attendees": []
},
...
]
}
Step 5: Reset to Clean State
Finally, we use release API to reset the sandbox to a clean state. This wipes all data and returns the sandbox to its original empty condition. It should also release this sandbox for future use.
Unlocking New Capabilities for AI Agent Development
This infrastructure is not just about testing; it enables entirely new workflows for AI development that were previously impossible or impractical.
1. Functional Benchmarking for AI Agents
How do you measure if a new model is better at using tools than the previous one? Static text benchmarks are insufficient for agents. IBM researchers reviewed 120 frameworks for evaluating LLM agents and found that "even the best-performing agents score as low as 5%" on challenging new benchmarks like OSWorld, AppWorld, and CRMWorld.
Klavis Sandboxes allow you to create deterministic functional benchmarks. You can define 100 specific tasks (e.g., "Reschedule conflicting meetings," "Archive old emails"), run them against a consistent starting state, and programmatically score the success rate based on the final Dump data.
Key benchmarking capabilities:
- Deterministic seeds and snapshots for reproducible evaluations
- Step-by-step environment state logs for debugging failures
- Cost and latency metrics alongside accuracy scores
- Parallel task execution for high-throughput evaluation
2. Reinforcement Learning (RL) Training Environments
Training models to use tools requires a reliable Action-Feedback loop. In a live environment, calculating the "reward" is difficult because the environment is noisy. RL environments are becoming critical for developing capable AI agents—leading AI labs are now demanding more RL environments for training agents on complex, multi-step tasks.
With a Klavis sandbox, you have perfect observability. You can train models using Reinforcement Learning by comparing the Dump (post-action state) against a Target State. If the delta matches the goal, the model receives a positive reward. This enables fine-tuning models specifically for tool usage and complex logic.
RL training features:
- Verifiable task completion through state comparison
- Multi-turn interaction support for complex agent workflows
- Scalable parallelization for distributed training
- Automated reward calculation based on state diffs
3. Safe Development Environments
Developers need a "localhost" for SaaS applications. When building a new feature that integrates with Slack, Jira, or Salesforce, testing in a production workspace risks spamming colleagues or corrupting data.
Klavis acts as your safe development environment. You can develop, break things, and test edge cases (like deleting root folders) with zero risk.
4. Debugging and Issue Reproduction
Debugging agent failures is notoriously difficult because context is often lost. With Sandbox-as-a-Service, you can reproduce issues reliably. If an agent fails a task, you can re-initialize the sandbox to the exact state where the failure occurred and replay the interaction step-by-step to identify the root cause.
Debugging capabilities:
- Complete audit logs of all agent actions
- Failure/error taxonomies for systematic analysis
- Deterministic vs. non-deterministic evaluation indicators
- Full state snapshots at any point in the interaction
Why MCP for Agent-Sandbox Interaction?
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open-source standard for connecting AI applications to external systems. Introduced by Anthropic in November 2024 and now supported by OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and major development platforms, MCP provides a universal adapter between AI agents and the tools they use.
Using MCP for sandbox interaction offers several advantages:
- Framework Agnostic: Works with LangChain, CrewAI, OpenAI Agents SDK, AutoGen, and custom implementations
- Standardized Tool Interface: Consistent API regardless of the underlying service
- Production Parity: Same MCP interface used in sandbox works in production
- Ecosystem Compatibility: Leverage the growing MCP server ecosystem
Scalability and Parallelism
For large-scale evaluations and training runs, Klavis provides proven parallelization capabilities:
- Concurrent sandbox instances: Run hundreds of isolated environments simultaneously
- No state collision: Each sandbox is completely isolated
- Automatic resource management: We handle scaling infrastructure automatically
- Cost-efficient: Pay only for active sandbox time
Security and Data Privacy
All Klavis sandbox environments include enterprise-grade security controls:
- Complete isolation: Each sandbox is containerized and isolated
- Ephemeral by design: Data is permanently erased on reset or session end
- No external connections required: Self-contained environments
- Audit logging: Complete traceability of all operations
Get Started
Klavis AI brings engineering rigor to the agentic workflow. We currently support 50+ production-ready Sandbox and MCP servers, covering the entire stack of modern SaaS applications and developer tools.
Supported Integrations
Klavis provides extensive coverage across critical environment domains:
| Domain Category | Supported Services |
|---|---|
| Productivity & Comms | Microsoft Teams, Slack, Discord, Asana, ClickUp, Monday, Motion, Cal.com, Confluence |
| Consumer Apps | Google Calendar, Outlook Calendar, Gmail, Outlook Mail, Notion, Google Docs, WordPress, WooCommerce, Shopify |
| Data & Knowledge | Postgres, Snowflake, Supabase, Google Sheets, Excel, Mem0, Airtable |
| General Utilities | Fetch, Filesystem, Memory, PDF Tools, Markdown2doc, Doc2markdown, Word, PowerPoint |
| Computer Use & Automation | Terminal, Playwright |
| Analytics & BI | Weights & Biases, Hugging Face |
| Cloud & Infra | Google Cloud, Kubernetes |
| Developer & DevOps | GitHub, Linear, Jira, Git, Google Forms |
| CRM & Business | Salesforce, HubSpot, QuickBooks, Moneybird, Close, Resend, Attio, Emails (Poste.io) |
| Storage | Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive |
Developer Tooling and Integration
Klavis provides comprehensive developer support:
- REST APIs with complete documentation
- Python SDK for native integration
- OpenAPI specification for code generation
- Detailed documentation and examples
- Dedicated technical support
View the Full API Documentation to get a comprehensive list of available sandboxes and their capabilities.
We are currently onboarding partners who want to build the next generation of reliable AI agents. If you want to try Sandbox-as-a-Service:
Contact the Klavis Team to get access.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How does this differ from a standard mock server? A: Standard mocks usually return static responses (e.g., always returning "200 OK"). A Klavis Sandbox is a stateful logic engine. If your agent uploads a file to the sandbox file system, that file actually exists in the virtual drive and can be retrieved or modified by subsequent commands.
Q: Can I use this for training custom models? A: Yes. The deterministic nature of the sandbox makes it ideal for generating synthetic training data or performing Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), as you can mathematically verify the outcome of every tool call.
Q: How do you handle environment versioning and reproducibility? A: Klavis supports deterministic seeds and snapshots for complete reproducibility. Each sandbox version is tracked, and you can replay evaluations against specific environment versions for consistent benchmarking over time.
Q: What verifier mechanisms do you provide to determine task success? A: Our dump API provides complete state snapshots that can be programmatically compared against expected outcomes. This enables automated verification pipelines with custom success criteria.
Q: Is the data private? A: Yes. All sandbox environments are isolated and ephemeral. Once you call Reset or the session ends, the data is permanently erased.
Q: How scalable is the platform for large-scale evaluations? A: Klavis supports full parallelization with proven large-scale task execution. You can run thousands of concurrent evaluations without state collision between sandbox instances.
